2025 AZ-305 Practical Analysis: Latest Practice Questions Breakdown and High-Score Strategies

Hello everyone!
Get ready, we’re about to dive into some practical insights for the AZ-305 exam.
Since the content is quite extensive, I’ve included anchor links for the article’s sections, so you can jump to the parts you want to read:
- AZ-305 Exam Overview and Latest Trends
- Key Focus Areas and Question Patterns of AZ-305
- Practice-Oriented Learning Strategies
- Latest Practice Questions Breakdown and Problem-Solving Techniques
- User Feedback and Exam Preparation Insights
- Personal Perspective from a Veteran IT Certification Blogger
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
AZ-305 Exam Overview and Latest Trends
1. Exam Positioning and Core Objectives
AZ-305 (Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions) is a core exam in Microsoft’s cloud architecture certification system, aimed at solution architects. Unlike the administrator-level AZ-104, it places greater emphasis on architecture-level design and trade-offs, testing candidates’ decision-making abilities across multiple dimensions (performance, security, compliance, and cost).
2. Latest Changes in the 2025 Exam Syllabus
Based on Microsoft’s 2025 exam blueprint, AZ-305 has been updated in the following areas:
- Security and Identity Authentication: Exam topics have been expanded, with increased focus on Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) and hybrid identity scenarios.
- Multi-Region High Availability: More questions related to Azure Front Door, Traffic Manager, and geographic redundancy.
- Cost and Governance: FinOps principles are emphasized for the first time, requiring candidates to not only understand technology but also consider budget optimization.
3. Cloud Computing and Architect Certification Market Demand
According to the Gartner 2025 report, global demand for cloud solution architects has grown by 18% year-over-year, with professionals holding Microsoft Azure advanced certifications earning an average salary 35% higher than typical cloud engineers. This makes AZ-305 not just a certificate, but a career accelerator.
Key Focus Areas and Question Patterns of AZ-305
1. Increased Emphasis on Architecture Design Scenario Questions
The AZ-305 exam questions are almost entirely scenario-driven, presenting a customer background, business requirements, and constraints, and requiring candidates to design the optimal solution.
2. Deep Integration of Security, Compliance, and Cost Optimization
For example, questions won’t simply ask “how to achieve high availability” but will incorporate budget constraints, requiring candidates to weigh the costs of different solutions.
3. Role of Microsoft’s Official Blueprint
Microsoft Learn has become a key reference for exam content. Real-world case studies and official best practices are almost always the basis for question design.
Practice-Oriented Learning Strategies
1. From “Rote Memorization” to “Understanding-Driven”
Many candidates rely on memorizing questions but struggle with rephrased questions during the exam due to the “question sea tactic.” The key lies in:
- Mastering design principles rather than memorizing answers.
- Solving problems by analyzing business requirements → identifying key constraints → comparing the pros and cons of options.
2. Case Studies vs. Practice Tests
- Case Studies: Review real-world architecture case studies to understand how enterprises resolve conflicts between performance and security.
- Practice Tests (AZ-305): Assess time management and improve on-the-spot problem-solving skills.
3. Time Management and Answering Strategies
- The AZ-305 exam has a moderate question volume (40–60 questions), so it’s recommended to tackle easier questions first.
- Scenario-based questions often have lengthy options, so use the elimination method effectively.
Latest AZ-305 Practice Questions Breakdown and Problem-Solving Techniques
Question 1:
HOTSPOT
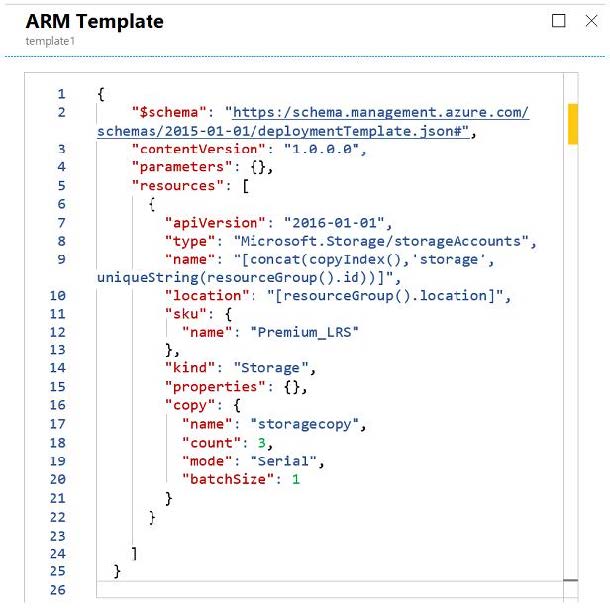
You have an Azure Resource Manager template named Template1 in the library as shown in the following exhibit.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Correct Answer:

Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-resource-manager/templates/template-syntax
Question 1: HOTSPOT Analysis
Question Background:
The scenario involves deploying resources using an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template named Template1. The template’s code is provided, and the task is to determine what can be specified during deployment and what Template1 deploys.
Key Constraints:
- The template includes a parameter apiVersion and a copy loop to create multiple storage accounts.
- The deployment is structured within a resource group, with a specified location and sku (Premium LRS).
- The copy loop iterates 3 times (count: 3), creating resources dynamically.
Option Comparison:
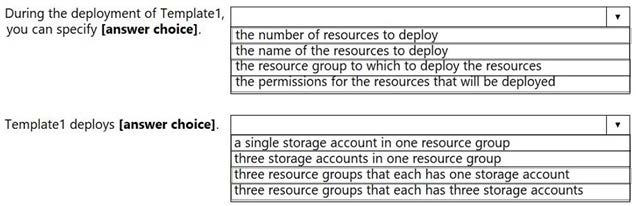
During the deployment of Template1, you can specify:
- The number of resources to deploy: The copy loop’s count is fixed at 3, so this cannot be changed dynamically during deployment.
- The name of the resources to deploy: The name uses concat(copyIndex(), …, which allows dynamic naming based on the index, but this is defined within the template, not specified during deployment.
- The resource group to which to deploy the resources: This can be specified during deployment via the ARM deployment process (e.g., via Azure CLI or Portal).
- The permissions for the resources that will be deployed: Permissions are not configurable during deployment; they are managed separately (e.g., via RBAC).
Template1 deploys:
- A single storage account in one resource group: The copy loop creates multiple accounts, so this is incorrect.
- Three storage accounts in one resource group: The copy loop with count: 3 suggests 3 storage accounts are created within a single resource group.
- Three resource groups that each has one storage account: The template deploys within one resource group, not multiple.
- Three resource groups that each has three storage accounts: This overcomplicates the deployment structure, which is not supported by the template.
Best Answer:
- During the deployment of Template1, you can specify: the resource group to which to deploy the resources.
- Template1 deploys: three storage accounts in one resource group.
Reasoning:
- The resource group is a deployment parameter that can be specified externally, aligning with ARM template flexibility.
- The copy loop with count: 3 indicates three storage accounts are created within the same resource group, as the resourceGroup() function applies to a single group.
Common Pitfalls:
- Ignoring the copy loop: Candidates might assume a single account is deployed, overlooking the copy iteration.
- Confusing resource group specification: Some might think the number of resources or their names can be specified, but these are template-defined.
- Overcomplicating structure: Assuming multiple resource groups are involved when the template targets one.
Question 2:
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
Your company has deployed several virtual machines (VMs) on-premises and to Azure. Azure ExpressRoute has been deployed and configured for on-premises to Azure connectivity.
Several VMs are exhibiting network connectivity issues.
You need to analyze the network traffic to determine whether packets are being allowed or denied to the VMs.
Solution: Use the Azure Advisor to analyze the network traffic.
Does the solution meet the goal?
A. Yes
B. No
Correct Answer: B
Question 2: Analysis
Question Background:
The scenario involves VMs deployed on-premises and in Azure, connected via Azure ExpressRoute, with some VMs experiencing network connectivity issues. The goal is to analyze network traffic to determine if packets are being allowed or denied.
Key Constraints:
- The solution must analyze network traffic at a detailed level (e.g., packet-level inspection).
- The tool must be suitable for troubleshooting connectivity issues in a hybrid environment.
Option Comparison:
Solution: Use the Azure Advisor to analyze the network traffic
- Pros: Azure Advisor provides best practice recommendations and optimizes resource configuration, performance, and cost.
- Cons: It does not offer real-time packet-level analysis or IP flow verification, which are needed to determine if packets are allowed or denied.
Correct Alternative: Use Azure Network Watcher with IP Flow Verify
- Pros: Network Watcher’s IP Flow Verify tool allows detailed analysis of network traffic, showing whether packets are permitted or blocked based on security rules.
- Cons: Requires setup and familiarity with the tool.
Best Answer:
- Does the solution meet the goal? B. No
- Reasoning: Azure Advisor is designed for optimization and best practices, not for real-time network traffic analysis or packet-level troubleshooting. Azure Network Watcher with IP Flow Verify is the appropriate tool for this task.
Common Pitfalls:
- Misunderstanding Advisor’s purpose: Candidates might assume Advisor handles all monitoring tasks, overlooking its focus on recommendations rather than diagnostics.
- Ignoring hybrid connectivity: Some might not consider tools suited for both on-premises and Azure environments.
- Overlooking specific tools: Failing to recognize Network Watcher’s specialized capabilities for traffic analysis.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/advisor/advisor-overview
Question 3:
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an app named App1 that uses data from two on-premises Microsoft SQL Server databases named DB1 and DB2.
You plan to move DB1 and DB2 to Azure.
You need to implement Azure services to host DB1 and DB2. The solution must support server-side transactions across DB1 and DB2.
Solution: You deploy DB1 and DB2 as Azure SQL databases on the same Azure SQL Database server.
Does this meet the goal?
A. Yes
B. No
Correct Answer: B
Question 3: Analysis
Question Background:
The scenario involves an app (App1) that uses data from two on-premises SQL Server databases (DB1 and DB2), planned to be moved to Azure. The solution must support server-side transactions across DB1 and DB2.
Key Constraints:
- The solution must enable server-side transactions (e.g., distributed transactions) between DB1 and DB2.
- The Azure services must support this transactional capability.
Option Comparison:
Solution: Deploy DB1 and DB2 as Azure SQL databases on the same Azure SQL Database server
- Pros: Hosting both databases on the same Azure SQL Database server simplifies management and ensures they are in the same environment.
- Cons: Azure SQL Database (PaaS) does not natively support distributed transactions across multiple databases, even on the same server, due to its architecture and limitations in cross-database transaction support.
Correct Alternative: Deploy DB1 and DB2 to SQL Server on an Azure virtual machine
- Pros: SQL Server on an Azure VM (IaaS) allows full control over the database engine, enabling distributed transactions and server-side transaction support across DB1 and DB2 when managed under the same ownership.
- Cons: Requires more management overhead compared to Azure SQL Database.
Best Answer:
- Does this meet the goal? B. No
- Reasoning: Azure SQL Database does not support server-side distributed transactions across databases, even on the same server. Deploying DB1 and DB2 to SQL Server on an Azure VM provides the necessary control to enable such transactions.
Common Pitfalls:
- Assuming same-server compatibility: Candidates might think placing databases on the same Azure SQL server enables transactions, overlooking PaaS limitations.
- Overlooking transaction requirements: Some might focus on migration ease rather than transactional needs.
- Misjudging IaaS vs. PaaS: Failing to recognize that IaaS offers more flexibility for complex transaction scenarios.
Reference:
https://docs.particular.net/nservicebus/azure/understanding-transactionality-in-azure
Question 4:
You are developing an application that will enable users to download content from an Azure Storage account.
The users must only be able to download the content for a period of seven days.
You need to recommend an authentication solution to access the storage account.
What should you include in the recommendation?
A. shared access signature (SAS) tokens
B. identity-based authentication that uses Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
C. storage access key
D. identity-based authentication that uses Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
Correct Answer: A
Question 4: Analysis
Question Background:
The scenario involves developing an application where users can download content from an Azure Storage account, with access restricted to a seven-day period.
Key Constraints:
- Access must be time-limited to seven days.
- The solution must ensure secure and controlled access to the storage account.
Option Comparison:
A. Shared Access Signature (SAS) tokens
- Pros: SAS tokens allow time-bound access (e.g., seven days) with customizable permissions, making them ideal for temporary access to storage resources.
- Cons: Requires proper management to avoid security risks if tokens are mishandled.
B. Identity-based authentication that uses Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
- Pros: Provides secure identity-based access.
- Cons: AD DS is on-premises and not natively designed for time-limited access to Azure Storage, requiring additional integration.
C. Storage access key
- Pros: Offers full access to the storage account.
- Cons: Keys provide unlimited access unless rotated, which doesn’t meet the seven-day restriction.
D. Identity-based authentication that uses Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
- Pros: Provides secure, identity-based access with Azure AD integration.
- Cons: Azure AD authentication does not natively support time-limited access for storage downloads without additional configuration (e.g., SAS or role-based access control with expiration).
Best Answer:
- What should you include in the recommendation? A. Shared Access Signature (SAS) tokens
- Reasoning: SAS tokens are designed to provide time-limited, granular access to Azure Storage, perfectly aligning with the seven-day requirement.
Common Pitfalls:
- Confusing access keys with time limits: Candidates might select storage access keys, overlooking their lack of time restriction.
- Overcomplicating with AD: Some might choose AD DS or Azure AD, not realizing they don’t directly address the time-bound access need without SAS.
- Ignoring SAS flexibility: Failing to recognize SAS as the standard solution for temporary storage access.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-sas-overview
Question 5:
You need to recommend a notification solution for the IT Support distribution group. What should you include in the recommendation?
A. Azure Network Watcher
B. an action group
C. a SendGrid account with advanced reporting
D. Azure AD Connect Health
Correct Answer: D
Question 5: Analysis
Question Background:
The scenario requires recommending a notification solution for the IT Support distribution group, though specific details about the context (e.g., what triggers the notification) are not provided. Based on the correct answer and reference, it likely relates to monitoring and notifying about Azure AD or hybrid identity health.
Key Constraints:
- The solution must support notifications for the IT Support group.
- It should align with Azure services relevant to monitoring or operational health.
Option Comparison:
A. Azure Network Watcher
- Pros: Monitors and diagnoses network issues.
- Cons: Focused on network traffic analysis, not general IT support notifications.
B. An action group
- Pros: Part of Azure Monitor, used to define notification recipients (e.g., email to a distribution group) for alerts.
- Cons: Requires integration with a monitoring service to trigger notifications.
C. A SendGrid account with advanced reporting
- Pros: Enables email notifications with detailed reporting.
- Cons: A third-party service, not natively optimized for Azure IT support notifications.
D. Azure AD Connect Health
- Pros: Monitors and provides notifications (e.g., via email to a distribution group) for Azure AD Connect health, aligning with IT support needs for hybrid identity management.
- Cons: Limited to Azure AD and sync health scenarios.
Best Answer:
- What should you include in the recommendation? D. Azure AD Connect Health
- Reasoning: Azure AD Connect Health is designed to monitor hybrid identity health and send notifications to IT support groups, making it a suitable solution based on the reference.
Common Pitfalls:
- Misjudging action groups: Candidates might choose an action group, thinking it handles notifications directly, but it needs a monitoring source like Azure AD Connect Health.
- Overcomplicating with SendGrid: Some might select SendGrid, overlooking its lack of native Azure integration for this use case.
- Focusing on network tools: Selecting Azure Network Watcher due to its monitoring role, but it’s irrelevant to IT support notifications.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/hybrid/how-to-connect-healthoperations
Question 6:
HOTSPOT
You plan to develop a new app that will store business critical data. The app must meet the following requirements:
1.
Prevent new data from being modified for one year.
2.
Maximize data resiliency.
3.
Minimize read latency.
What storage solution should you recommend for the app? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Correct Answer:
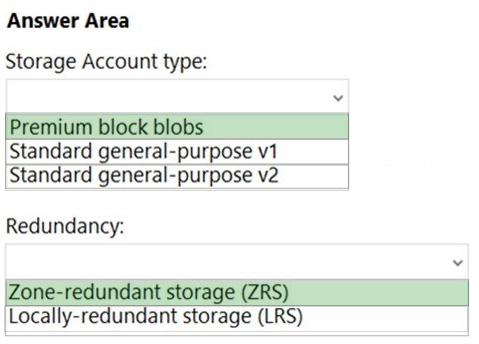
Question 6: HOTSPOT Analysis
Question Background:
The scenario involves developing a new app that stores business-critical data with the following requirements:
- Prevent new data from being modified for one year.
- Maximize data resiliency.
- Minimize read latency.
Key Constraints:
- Data immutability for one year (e.g., preventing modifications).
- High data resiliency to ensure availability and durability.
- Low read latency for optimal performance.
Option Comparison:
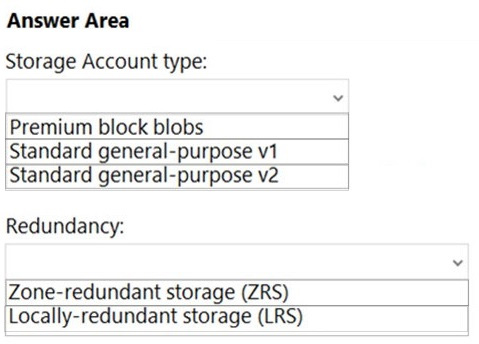
Storage Account Type:
- Premium block blobs: Offers high performance and low latency, ideal for minimizing read latency, but lacks built-in immutability features. Requires additional configuration (e.g., Azure Blob Immutability Policies).
- Standard general-purpose v1: Older version with limited scalability and performance, not optimal for minimizing read latency.
- Standard general-purpose v2: Provides a balance of performance, scalability, and cost, with support for immutability policies (e.g., Legal Hold or Time-Based Retention) to prevent data modification for one year.
Redundancy:
- Zone-redundant storage (ZRS): Replicates data across multiple availability zones in a region, maximizing resiliency and availability.
- Locally-redundant storage (LRS): Replicates data within a single data center, offering less resiliency compared to ZRS.
Best Answer:
- Storage Account Type: Standard general-purpose v2
- Redundancy: Zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
- Reasoning:
- Standard general-purpose v2 supports Azure Blob Immutability Policies (e.g., Time-Based Retention) to prevent data modification for one year, while offering good performance to minimize read latency.
- ZRS maximizes data resiliency by replicating data across zones, ensuring high availability even if one zone fails.
Common Pitfalls:
- Choosing Premium block blobs: Candidates might select this for low latency, overlooking the lack of native immutability without additional configuration.
- Selecting LRS: Some might pick LRS for cost savings, missing the resiliency requirement.
- Ignoring immutability: Failing to recognize that Standard v2 with immutability policies meets the one-year modification lock.
…
More Latest AZ-305 Practice Questions
| Free Download | Explain | Total Questions |
| AZ-305 PDF | Newbies can practice the test according to my analysis method | https://www.leads4pass.com/az-305.html (378 Q&A) |
User Feedback and Exam Preparation Insights
- High-Scoring Candidate Experience: 2 hours of daily study + one mock exam per week → pass in 2.5 months.
- Common Pitfalls: Only practicing questions without understanding scenarios → failure when real questions are slightly modified.
- Community Value: Reddit, Microsoft Official Community, and LinkedIn Study Group are treasure troves for knowledge sharing.
My Perspective
- AZ-305 is a must for architects; it tests not just knowledge but also thinking.
- My experience: Learn through real projects + practice with mock exams.
- After passing AZ-305, you’re not just “certified” but a “practical architect.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How does the difficulty of AZ-305 compare to AZ-104 and AZ-700?
Answer: AZ-305 focuses more on architectural and design thinking, while AZ-104 emphasizes operations and management.
Q2: How long does it take to prepare for AZ-305?
Answer: On average, 2-3 months, depending on your project experience.
Q3: How should I combine official materials with third-party question banks?
Answer: Recommended: Start with Microsoft Learn → then practice with high-quality question banks.
Q4: Is it worth taking the exam in one go vs. in stages?
Answer: Those with project experience can attempt it in one go; otherwise, take it in steps (AZ-104 first, then AZ-305).
Q5: How can I balance work and exam preparation?
Answer: Set fixed study schedules to avoid last-minute cramming.
Q6: What are the career paths after passing AZ-305?
Answer: You can advance to roles like Cloud Architect, Technical Consultant, or Cloud Solutions Specialist.
Conclusion
The 2025 AZ-305 exam emphasizes practical thinking, requiring candidates to:
- Shift from “rote memorization” to “understanding architectural trade-offs.”
- Validate learning with real-world cases and use mock exams for practice.
- Leverage user feedback and community resources to boost preparation efficiency.
As an experienced IT certification blogger, my advice is:
Focus on understanding, drive with practical experience, and test through exams.
This way, you’ll not only earn the certification but also grow into a true cloud architect.